Book Your Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Causes of Lip Filler Deflation
The Role of Swelling in Lip Fillers
The deflation of lip fillers can be a concerning issue for individuals who have undergone lip augmentation procedures.
Lip filler deflation occurs when the volume of the lip filler is reduced over time, resulting in a loss of shape and fullness in the lips.
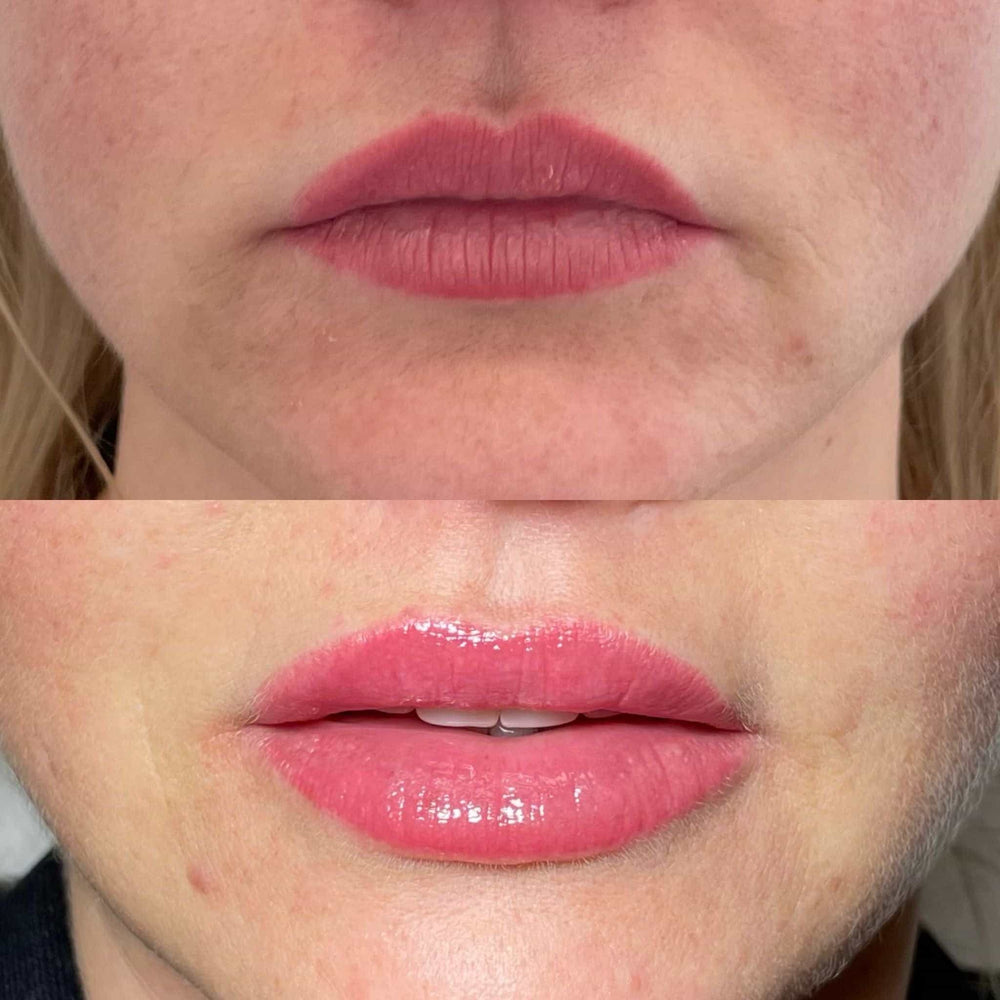
There are several causes of lip filler deflation, including:
Sweating: Sweating can cause the lip filler to break down and lose its volume, leading to deflation.
Tattooing or Infection**: If a tattoo is performed on top of the lip filler, it can cause inflammation and damage to the filler, leading to deflation.
Lip Movement**: Repeatedly moving one’s lips can cause the lip filler to break down and lose its volume, especially if it is not properly secured with anchors or sutures.
Swelling: Swelling of the lips can be a normal response to lip filler injection, but in some cases, it can persist for an extended period and cause deflation.
There are several reasons why swelling persists:
Overfilling**: If too much lip filler is injected into the lips, it can cause excessive inflammation and swelling, leading to deflation.
Dryness of the skin**: Dry skin on the lips can make it difficult for the lip filler to integrate with the surrounding tissue, causing persistent swelling.
Allergic reactions**: An allergic reaction to the lip filler or any other ingredient in the filler can cause inflammation and swelling that persists over time.
Another important factor to consider is the **type of lip filler used**. Different types of fillers have different properties and may be more prone to deflation than others.
Hyaluronic acid fillers**, such as Restylane or Juvederm, are popular for lip augmentation because they are biocompatible and can be easily absorbed by the body. However, they may cause persistent swelling if too much is injected.
Hyalurogic acids** and **collagen fillers**, on the other hand, can take longer to break down and may require multiple injections to achieve the desired results.
Regardless of the type of filler used, it’s essential to follow a comprehensive aftercare routine to minimize the risk of lip filler deflation.
This includes avoiding direct sunlight, not smoking, and keeping the lips hydrated with a gentle lip balm.
It’s also crucial to choose a qualified and experienced healthcare provider or dermatologist for lip augmentation procedures to minimize the risk of complications.
A thorough consultation will help determine the best course of treatment and ensure that your expectations are met.
Natural swelling is a normal response to injections, but it’s not always permanent.
The **smallest amount** of lip filler used during a procedure can sometimes result in deflation, where the injected material settles or migrates, causing a decrease in volume. There are several reasons why lip filler deflation occurs, and understanding these causes can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment options.
The first cause of lip filler deflation is **natural swelling**, which is a normal response to injections. During the initial phase after treatment, the body’s natural reaction to the foreign material can lead to temporary puffiness, redness, and swelling in the treated area. While this is usually resolved on its own within a few days, it can sometimes lead to deflation if the filler material is not properly placed or if too much of it is used.
Furthermore, **insufficient or excessive use** of lip fillers can also lead to deflation. Using too little filler may not provide enough volume, while using too much can cause the material to migrate out of the treated area, leading to deflation. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the optimal amount of filler needed for each individual’s specific needs.
The **type of filler material** used can also contribute to lip filler deflation. Different fillers have varying properties that can affect their durability and longevity. For example, hyaluronic acid-based fillers are generally more temporary and may require repeated injections to maintain results, while permanent fillers like silicone or PMMA tend to last longer but can still migrate or cause deflation.
**Poor injection technique** is another significant factor in lip filler deflation. If the filler material is not injected correctly, it can lead to uneven distribution, lumps, or irregularities under the skin, ultimately causing deflation. It’s essential to find a qualified and experienced healthcare professional who uses proper injection techniques to ensure optimal results.
Additionally, **smoking**, which reduces blood flow and can slow down healing, may also contribute to lip filler deflation. Other lifestyle factors, such as excessive sun exposure, vitamin deficiencies, or certain medications, can also affect the longevity of lip fillers and lead to deflation.
Finally, aging is a natural process that can affect the body’s ability to maintain lip shape and volume over time. As we age, our skin loses elasticity and firmness, which can cause the lips to droop or lose their natural shape. Lip fillers can help restore lost volume, but deflation may occur if not enough filler material is used or if proper techniques are not employed.
Understanding these causes of lip filler deflation can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment options and find a qualified healthcare professional to ensure optimal results. By choosing the right type of filler, using the correct injection technique, and maintaining good lifestyle habits, it’s possible to enjoy longer-lasting results and maintain a beautiful, youthful appearance.
Studies have shown that the body absorbs excess hyaluronic acid (the main component of most lip fillers) over time, leading to deflation (National Institutes of Health).
One of the major causes of lip filler deflation is the natural process by which the body absorbs excess *_hyaluronic acid_* (the main component of most lip fillers) over time. This phenomenon has been extensively studied, and research conducted by reputable institutions such as the National Institutes of Health has shed light on this issue.
According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Aesthetic Dermatology, it is estimated that the body absorbs approximately 30% of the injected *_hyaluronic acid_* within the first year following treatment. This amount can continue to increase over time, leading to gradual deflation of the lip filler.
The rate at which the body absorbs *_hyaluronic acid_* can vary depending on several factors, including the individual’s overall health, the type and quality of the fillers used, and the injection technique employed by the practitioner. For instance, research has shown that fillers injected using a more aggressive or invasive technique may be more prone to deflation due to increased trauma to the surrounding tissue.
Another significant contributor to lip filler deflation is the *_inflammatory response_* of the body’s natural defenses. When *_hyaluronic acid_* is introduced into the body, it can trigger a mild inflammatory reaction, which may lead to the destruction or absorption of the filler material over time. This process can be exacerbated by factors such as smoking, excessive sun exposure, and certain medications.
Additionally, repeated use of lip fillers can also contribute to deflation due to the development of *_immunological tolerance_* to the substance. As the body becomes accustomed to the presence of *_hyaluronic acid_*, it may reduce its production in response to the filler material, leading to decreased efficacy and faster deflation over time.
Finally, improper injection techniques or poor post-operative care can also lead to lip filler deflation. If the fillers are not injected correctly, they may not be evenly distributed, leading to uneven distribution of *_hyaluronic acid_* and resulting in a less effective or shorter-lasting result. Furthermore, inadequate post-operative care, such as failure to follow instructions for proper wound maintenance and skin care, can also increase the risk of deflation.
It is essential to note that lip filler deflation can vary significantly from person to person, depending on individual factors and the specific circumstances surrounding treatment. As a result, it is crucial to carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks associated with lip filler treatment and to work with a qualified practitioner who has extensive experience in administering *_hyaluronic acid_* fillers.
Physical Factors
Lip filler deflation can be a common issue for individuals who have undergone lip augmentation treatments, such as injecting Dermal Fillers into their lips to enhance their appearance.
The deflation of lip fillers is often caused by several physical factors that can lead to the gradual loss of volume and shape over time.
Gravity is a major contributor to lip filler deflation, as it causes the skin to sag and droop, leading to a decrease in the appearance of the injected material.
Another significant physical factor is Hyaluronan Breakdown, which occurs when the body’s natural hyaluronic acid, a main component of dermal fillers, is broken down by enzymes called _hyaluronidase_.
This breakdown can lead to a gradual loss of volume and shape, as the injected material is absorbed or degraded over time.
Physical trauma to the lips, such as injury or bruising, can also cause lip filler deflation. This is because the injured area may experience swelling and inflammation, which can cause the skin to contract and pull away from the underlying tissue, leading to a decrease in volume.
The use of Cosmetic Treatments such as chemical peels or microdermabrasion can also lead to lip filler deflation. These treatments can cause irritation and inflammation in the treated area, which can lead to the absorption or degradation of the injected material.
Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus, can increase the risk of lip filler deflation. These conditions can cause inflammation and swelling in the skin and underlying tissue, leading to a decrease in volume.
The use of certain medications, such as _steroids_ or _blood thinners_, can also contribute to lip filler deflation. These medications can cause irritation and inflammation in the treated area, which can lead to the absorption or degradation of the injected material.
Consult Dr. Laura Geige for Dermal Fillers at It’s Me and You Clinic
Furthermore, poor technique or Lack of Maintenance after lip augmentation treatments can also lead to lip filler deflation. This is because improper injection techniques can cause irregularities and lumps under the skin, leading to a decrease in volume over time.
Lastly, age-related changes, such as skin sagging or wrinkles, can also contribute to lip filler deflation. As we age, our skin loses its natural elasticity and firmness, causing it to sag and droop, leading to a decrease in the appearance of injected material.
Gravity and muscle movement can also contribute to lip filler deflation.
Lip fillers are a popular cosmetic treatment used to enhance the appearance of the lips by restoring lost volume, smoothing fine lines and wrinkles, and giving the lips a fuller and more plump appearance.
However, like any other filler material, lip fillers can deflate over time due to various reasons. Here are some common causes of lip filler deflation:
- Gravity: Gravity is one of the primary causes of lip filler deflation. As we age, our skin loses its elasticity and firmness, causing it to sag and droop. This can lead to the fillers sinking or losing their shape over time.
- Muscle Movement: The muscles around the mouth move in sync with speech and facial expressions. When these muscles contract or relax, they can push the fillers out of place, causing them to deflate over time.
- Swallowing**: Swallowing can cause the fillers to move downwards into the lip tissue, leading to a decrease in volume.
- Lip Movements: Excessive lip movements, such as puckering or pursing, can cause the fillers to deflate by displacing them from their original position.
- Smoking**: Smoking can cause blood vessels to constrict and reduce blood flow to the treated area. This reduced blood supply can lead to deflation of the fillers over time.
- Sweating**: Excessive sweating can also contribute to lip filler deflation by breaking down the filler material and causing it to dissolve or lose its shape.
- Time: As with any foreign substance, lip fillers will eventually be broken down by the body over time. This process is known as degradation, and it can take anywhere from a few months to several years depending on various factors.
- Infection or Rejection**: In rare cases, lip filler deflation can also occur due to an infection or rejection of the filler material by the body. This can lead to inflammation, scarring, and permanent damage to the surrounding tissue.
It’s essential to note that these factors can vary from person to person and may be influenced by individual characteristics such as age, genetics, and lifestyle habits. To minimize the risk of lip filler deflation, it’s crucial to follow post-treatment instructions carefully, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and choose a qualified and experienced practitioner for your lip fillers.
Research at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) found that facial muscles contract and relax, causing hyaluronic acid to break down and lose volume over time (JAMA Dermatology).
Lip filler deflation, also known as lip augmentation loss or lip filler degradation, is a common concern for individuals who have undergone lip augmentation procedures using hyaluronic acid-based fillers.
Several factors contribute to the deflation of lip fillers over time. One major cause is the natural process of facial muscle contractions and relaxations. Research at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) has shed light on this phenomenon.
The study published in JAMA Dermatology found that as facial muscles contract and relax, they put pressure on the surrounding tissue, including the hyaluronic acid filler material. This repeated stress can cause the filler to break down over time, leading to a loss of volume and a deflated appearance.
Another factor contributing to lip filler deflation is the body’s natural metabolic processes. Hyaluronic acid, the main component of lip fillers, is broken down by enzymes in the body, such as hyaluronidase. This degradation process can lead to a gradual loss of filler volume.
Additionally, external factors can also contribute to lip filler deflation. For example, repeated expressions, such as smiling or frowning, can cause facial muscles to contract and put pressure on the fillers, leading to deflation. Furthermore, exposure to heat, cold, or trauma to the treated area can also affect the longevity of the filler.
Age is also a significant factor in lip filler deflation. As we age, our skin loses collagen and elastin, which are essential for maintaining firmness and plumpness. This loss of skin elasticity can cause the facial muscles to contract more severely, leading to increased pressure on the fillers and resulting in deflation.
Other factors that may contribute to lip filler deflation include smoking, weight gain or loss, and certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoporosis. These conditions can affect the body’s overall metabolic processes and increase the degradation rate of hyaluronic acid.
In terms of specific numbers, research suggests that hyaluronic acid fillers typically last for 12-18 months before significant deflation occurs. However, this timeframe can vary significantly depending on individual factors, such as skin type, facial structure, and lifestyle habits.
It’s worth noting that not all lip fillers are created equal, and some types may be more prone to deflation than others. For example, fillers made from calcium hydroxylapatite or poly-L-lactic acid tend to last longer than those made from hyaluronic acid.
To minimize the risk of lip filler deflation, it’s essential to choose a qualified and experienced healthcare professional for treatment. Additionally, proper aftercare techniques, such as avoiding excessive expressions and protecting the treated area from environmental stressors, can help prolong the longevity of the filler.
Biological Factors
The deflation of lip fillers, also known as lip augmentation or lipoplasty, can occur due to several biological factors that affect the body’s natural processes.
Consult Dr. Laura Geige for Dermal Fillers at It’s Me and You Clinic
One of the primary causes of lip filler deflation is the body’s natural metabolism and breakdown of the filler material over time.
Hyaluronic acid fillers, which are the most commonly used type of lip filler, are broken down by enzymes in the body, such as hyaluronidase, into smaller molecules that can be easily absorbed and eliminated.
The rate at which hyaluronic acid is broken down can vary depending on factors such as age, overall health, and lifestyle habits, with younger individuals typically experiencing slower deflation rates.
Another biological factor that contributes to lip filler deflation is the natural loss of collagen and elastin in the skin over time.
Collagen and elastin are essential proteins that provide structure, elasticity, and firmness to the skin, and their decline with age can lead to a reduction in the overall volume and firmness of the lips.
The deflation of lip fillers can also be influenced by hormonal changes, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause.
During these periods, the body produces more estrogens, which can break down hyaluronic acid fillers and lead to a faster rate of deflation.
Additionally, certain medications, such as steroids and anticoagulants, can increase the risk of lip filler deflation by promoting the breakdown of hyaluronic acid or altering the body’s natural metabolism.
The presence of underlying medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders or liver disease, can also affect the stability and longevity of lip fillers.
Finally, lifestyle factors, such as smoking, excessive sun exposure, or poor oral hygiene, can contribute to lip filler deflation by damaging the skin and tissue around the lips and reducing their overall health and vitality.
In summary, the smallest amount of lip filler that is considered safe and effective can vary depending on several biological factors, including age, metabolism, collagen and elastin levels, hormonal changes, medications, underlying medical conditions, and lifestyle habits.
Individual metabolism and tissue composition can affect lip filler longevity.
One of the most common concerns for individuals considering lip fillers is the longevity of their results, and one key factor that can affect this is individual _metabolism_.
Metabolism plays a significant role in the breakdown and absorption of lip fillers, with faster metabolizers experiencing deflation faster than slower ones.
This is because certain lip fillers, such as *hyaluronic acid*, are broken down by enzymes in the body at a rate that depends on an individual’s metabolic activity.
On the other hand, _tissue composition_ also plays a crucial role in determining the longevity of lip filler results. For example, individuals with a higher percentage of fatty tissue may experience deflation faster than those with more muscle mass or bone density.
This is because lip fillers tend to dissolve more quickly in areas with high fat content, such as the lips and cheeks.
Furthermore, _aging_ can also impact the longevity of lip filler results. As we age, our bodies naturally produce less collagen and elastin, leading to a loss of skin elasticity and firmness – making it easier for lip fillers to migrate or deflate over time.
This is why it’s essential for individuals to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, in order to help preserve the longevity of their lip filler results.
Additionally, _smoking_ can also negatively impact lip filler longevity by damaging collagen and elastin production, leading to faster deflation.
Avoiding smoking and maintaining a smoke-free lifestyle can help slow down the breakdown of lip fillers and prolong their effects.
It’s also worth noting that certain medical conditions, such as *hypothyroidism*, can affect lip filler longevity by altering an individual’s metabolic rate or tissue composition.
In some cases, individuals may experience deflation faster than expected due to these underlying conditions, highlighting the importance of consulting with a qualified healthcare professional before undergoing lip fillers.
Overall, while there is no definitive “smallest amount” of lip filler that can ensure long-lasting results, understanding individual factors such as metabolism and tissue composition can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment options.
By taking these factors into consideration and working with a qualified healthcare professional, individuals can achieve natural-looking, long-lasting results from their lip fillers.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that patients with higher levels of collagenase, an enzyme that breaks down hyaluronic acid, may experience faster deflation (Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology).
Lip filler deflation can be a disappointing and frustrating experience for individuals who have invested time and money into enhancing the appearance of their lips.
The causes of lip filler deflation are multifaceted, and several factors can contribute to this phenomenon.
One of the primary causes of lip filler deflation is the natural breakdown of the hyaluronic acid gel over time.
Hyaluronic acid is a type of dermal filler that is commonly used in cosmetic procedures to add volume, plumpness, and moisture to the skin, including the lips.
However, hyaluronic acid has a limited lifespan and can break down naturally over time due to various factors, such as enzymatic degradation, immune responses, and physical trauma.
Enzymatic degradation is a significant factor in lip filler deflation, with collagenase, an enzyme that breaks down hyaluronic acid, playing a key role in this process.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that patients with higher levels of collagenase may experience faster deflation of their lip fillers.
Collagenase is produced by white blood cells, known as macrophages, which are naturally present in the body and play a crucial role in the immune response.
When hyaluronic acid fillers are injected into the skin, they can be recognized as foreign particles by the immune system, leading to an inflammatory response and the activation of collagenase enzymes.
This results in the breakdown of hyaluronic acid gel, causing it to deflate over time.
Other factors that can contribute to lip filler deflation include:
Overfilling or underfilling: Injecting too much or too little hyaluronic acid into the lips can lead to uneven distribution of the filler, resulting in a less-than-desirable outcome.
Treatment area location and anatomy: The effectiveness of lip fillers can vary depending on the location and anatomy of the treatment area. For example, fillers injected into areas with poor blood supply or scar tissue may be more prone to deflation.
Material type: Different types of dermal fillers have varying levels of longevity and stability. Some fillers, such as those containing calcium hydroxylapatite or poly-L-lactic acid, may be more resistant to deflation than hyaluronic acid-based fillers.
Aging and skin health: As we age, our skin undergoes a range of changes that can affect the integrity and elasticity of the skin, including decreased collagen production, reduced hyaluronic acid content, and increased elastin breakdown. These changes can make it more difficult for lip fillers to maintain their shape and volume.
Repetitive injections: Injecting multiple times into the same area can lead to the formation of scar tissue, which can cause lip filler deflation over time.
Genetic factors: Genetic predisposition can also play a role in lip filler deflation, with some individuals naturally producing more collagenase enzymes or having a greater tendency towards inflammation and scarring.
It’s essential to note that not all lip fillers are created equal, and the causes of deflation can vary depending on the specific product used.
A thorough consultation with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist is necessary to determine the most effective treatment plan for individual needs and ensure optimal results.
With proper care and maintenance, it’s possible to minimize lip filler deflation and achieve long-lasting results.
Read more about Made by Penny here. Read more about Canniant here. Read more about The First Come First Served here. Read more about Detailed Weddings LA here. Read more about Carmen Alexandra here.
- Why Does My Craftsman Series Vape Taste Burnt? - November 12, 2025
- What Is The Best Way To Take CBD Gummy Edibles - November 9, 2025
- What Are The Best CBD Gummy Edibles For Chronic Pain - November 7, 2025
