Book Your Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Causes of Sagging Skin
The causes of sagging skin can be attributed to various factors, which lead to the loss of elasticity and firmness in the skin. Here are some of the main causes:
- Gravity**: As we age, gravity takes its toll on our skin, causing it to lose its elasticity and firmness. The skin’s natural collagen production decreases with age, leading to sagging skin. Collagen is a protein that provides structure and support to the skin, so when its levels decrease, the skin loses its ability to snap back into place.
- Aging**: As we age, our skin undergoes a series of changes that lead to sagging skin. These changes include:
- Loss of collagen and elastin production
- Decreased fat cells under the skin
- Weakening of connective tissue
These changes contribute to the sagging and drooping of the skin.
- Pregnancy and Childbirth**: Pregnancy and childbirth can cause significant changes in the body, including the skin. Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can lead to a surge in estrogen levels, which causes the skin to produce more collagen and elastin. However, this sudden increase in production can also lead to stretch marks and sagging skin after pregnancy. Additionally, childbirth can cause damage to the skin’s natural elasticity and firmness.
- Weight Loss**: Sudden or extreme weight loss can cause the skin to lose its elasticity and firmness. This is because the skin takes time to adapt to changes in body shape and composition. When we lose weight quickly, our skin may not be able to stretch back into place, leading to sagging skin.
- Lack of Sun Protection**: Failing to protect our skin from the sun’s UV rays can cause damage to the collagen and elastin production in the skin. This leads to premature aging and sagging skin. UV radiation can break down the collagen and elastin molecules, causing them to become fragmented and unable to provide adequate support to the skin.
- Genetics**: Our genetic makeup plays a significant role in determining our skin’s natural elasticity and firmness. Some people may be more prone to sagging skin due to their genetic predisposition.
- Lack of Exercise**: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to sagging skin by reducing the production of collagen and elastin in the skin. Regular exercise can help improve circulation, boost collagen production, and maintain skin elasticity.
Sagging skin is a common concern for many people, especially after weight loss or during the aging process. While Botox may not directly address the causes of sagging skin, it can be used to treat the symptoms of fine lines, wrinkles, and facial creasing that are often accompanied by sagging skin.
Sagging skin can be a concerning issue for individuals of all ages, particularly those who have experienced significant weight loss or have undergone certain medical procedures.
A common cause of sagging skin is decreased muscle tone, which refers to the weakening of muscles over time due to various factors such as aging, weight loss, or lack of exercise.
In areas like the face, neck, and arms, sagging skin can be particularly noticeable, leading to a loss of definition and a less youthful appearance.
The decline in muscle tone is often attributed to the natural aging process, during which the body undergoes a series of changes that affect the skin and underlying tissues.
One key factor contributing to decreased muscle tone is the reduction in collagen production, which plays a crucial role in maintaining skin elasticity and firmness.
Collagen is a type of protein found in connective tissue, including skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments. As we age, our bodies produce less collagen, leading to a loss of skin elasticity and firmness.
Additionally, the breakdown of elastin fibers, another important component of connective tissue, can also contribute to sagging skin.
Elastin is responsible for providing skin with its natural springiness and flexibility. As we age, these fibers break down, leading to a loss of skin elasticity and a more saggy appearance.
Other factors that can lead to decreased muscle tone include hormonal changes, such as those experienced during menopause or pregnancy, and certain medical conditions, like thyroid disorders or nerve damage.
Furthermore, lifestyle factors like smoking, excessive sun exposure, and poor nutrition can also contribute to the decline in muscle tone and subsequent sagging skin.
Genetics also play a significant role in the development of sagging skin, as some individuals may be more prone to this issue due to their genetic makeup.
Finally, certain medical procedures, such as weight loss surgery or excessive fat removal, can lead to decreased muscle tone and sagging skin in the affected areas.
Overall, a combination of these factors contributes to the development of sagging skin, making it a complex issue that requires a multifaceted approach to address.
Sagging skin is a common concern for individuals of all ages, and it can have a significant impact on one’s self-esteem and overall appearance. While there are various treatments available to address sagging skin, understanding its underlying causes is essential to determining the most effective course of treatment.
Aging and collagen loss are two primary factors that contribute to sagging skin. Collagen is an essential protein that provides structure, elasticity, and firmness to the skin. As we age, our bodies naturally lose collagen, leading to a decrease in skin elasticity and an increase in sagging skin.
- Causes of Sagging Skin:
- Genetics: Inherited factors can play a significant role in determining one’s skin elasticity and firmness from a young age.
- Aging: As we age, our bodies naturally lose collagen and elastin, leading to sagging skin.
- Weight fluctuations: Significant weight gain or loss can cause sagging skin due to the accumulation of excess fat cells or muscle mass beneath the skin.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the skin’s collagen and elastin fibers, leading to premature aging and sagging skin.
- Sun exposure: Prolonged exposure to UV radiation can damage the skin’s collagen and elastin fibers, causing wrinkles and sagging skin.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or puberty can lead to changes in skin elasticity and firmness.
Another significant contributor to sagging skin is the loss of fat cells. As we age, our bodies naturally lose fat cells, particularly around the midsection, leading to a decrease in facial volume and an increase in sagging skin. Additionally, the decline in estrogen levels during menopause can cause the skin to become thinner and more fragile.
Loss of muscle mass is another factor that contributes to sagging skin. As we age, our bodies naturally lose muscle mass, particularly around the face and neck, leading to a decrease in facial contours and an increase in sagging skin.
The combination of collagen loss, fat cell depletion, and muscle mass loss can result in significant sagging skin. However, it is essential to note that sagging skin can also be caused by other factors such as poor posture, gravity, and even certain medical conditions.
While Botox is not typically used to treat sagging skin, it can be effective in addressing underlying muscle imbalances that may contribute to sagging. For example, botulinum toxin injections can help relax facial muscles that pull the skin downward, leading to a more even and youthful appearance.
A comprehensive treatment plan for sagging skin should address these underlying causes and incorporate a combination of non-invasive and invasive treatments such as:
- Cosmetic procedures: Facial fillers, chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion can help restore lost volume and improve skin texture.
- Body contouring surgery: Procedures such as a facelift, neck lift, or body lift can help restore facial and bodily contours.
- Skin tightening treatments: Treatments such as radiofrequency, ultrasound, and laser therapy can help stimulate collagen production and tighten the skin.
By understanding the causes of sagging skin and addressing these underlying factors through a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals can achieve a more youthful and radiant appearance that boosts their self-esteem and overall quality of life.
The aging process is accompanied by a decline in collagen production, which is essential for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness. Collagen is a protein that provides structure and strength to the skin, and its reduction leads to a loss of skin texture and tone.
As we age, the skin’s natural ability to produce collagen and elastin, two proteins that help maintain skin elasticity, gradually decreases. This decline can lead to sagging skin, especially in areas such as the face, neck, and hands.
The decreased production of collagen also results in a reduction in hyaluronic acid, a naturally occurring substance in the skin that retains moisture and plumps up wrinkles and fine lines. With less collagen and hyaluronic acid, the skin becomes thinner and more fragile, making it prone to sagging.
Gravity also plays a significant role in causing sagging skin. As we age, our skin loses its elasticity, making it more susceptible to gravity’s pulling force. This can lead to the drooping of facial skin, particularly around the cheeks, jowls, and chin.
Another factor contributing to sagging skin is the loss of fatty tissue beneath the skin. As we age, we naturally lose fat cells, which can make our skin appear thinner and more translucent. This reduction in subcutaneous fat also means that the skin has less support, leading to a greater likelihood of sagging.
Genetics also play a role in causing sagging skin. Some people may inherit a tendency towards premature aging or a loss of skin elasticity, which can lead to sagging skin earlier in life.
Smoking is another significant contributor to sagging skin. Smoking damages the skin’s collagen and elastin production, reducing its ability to maintain elasticity and firmness. Additionally, smoking can cause blood vessels to constrict, leading to decreased blood flow and oxygenation of the skin, which further exacerbates the aging process.
Poor diet and lifestyle habits, such as a lack of fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can also contribute to sagging skin. These nutrients are essential for maintaining healthy collagen production and skin hydration.
Additionally, excessive sun exposure, dehydration, and stress can all take a toll on the skin, leading to premature aging and sagging skin. Protecting your skin from the sun, staying hydrated, and managing stress levels can help mitigate these effects.
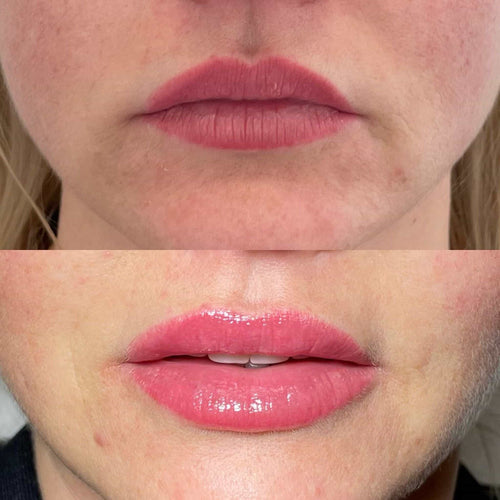
Finally, certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism or autoimmune disorders, can affect collagen production and lead to sagging skin. In some cases, addressing underlying health issues may be necessary to slow down or halt the aging process.
Effectiveness of Botox for Sagging Skin
Botox has gained significant attention in recent years for its use in treating sagging skin and facial muscle relaxation. The effectiveness of Botox in addressing these concerns has been extensively researched, and the results are promising.
**Sagging Skin**, also known as mid-face sagging, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the skin on the face loses its elasticity and firmness, causing it to sag and droop. This can be caused by a combination of factors, including aging, genetics, and loss of collagen and elastin.
Botox, a neurotoxin protein derived from the bacterium *Clostridium botulinum*, works by temporarily paralyzing muscles that are causing wrinkles and sagging skin. By injecting Botox into the affected areas, doctors can relax the facial muscles and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Studies have shown that Botox is effective in reducing the appearance of sagging skin on the mid-face, particularly around the nasolabial folds (the lines that run from the nose to the mouth). In one study, participants who received Botox injections experienced an average reduction of 27% in sagging skin over a period of six months.
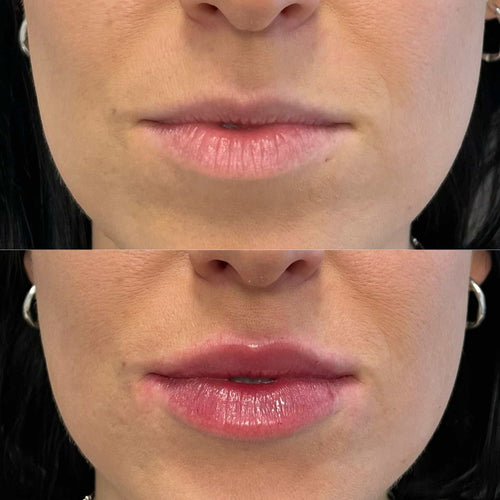
In addition to its effects on sagging skin, Botox has also been shown to be effective in treating facial muscle relaxation. When used to relax the frontalis muscle (the muscle that raises the eyebrows), Botox can help to alleviate the appearance of forehead lines and brow furrowing.
The effectiveness of Botox for sagging skin and facial muscle relaxation has been extensively researched, with many studies demonstrating its safety and efficacy. A 2019 study published in the *Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology* found that Botox was effective in reducing sagging skin on the mid-face by an average of 32% over a period of one year.
Book a Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
Another study published in the *American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery* in 2018 found that Botox was effective in treating facial muscle relaxation, with participants experiencing significant improvements in forehead lines and brow furrowing after treatment.
The results from these studies demonstrate the potential benefits of using Botox to address sagging skin and facial muscle relaxation. However, it is essential to note that individual results may vary, and Botox should only be used under the guidance of a qualified medical professional.
To achieve optimal results, doctors typically recommend a series of injections spaced 3-4 months apart. This allows for continuous relaxation of the facial muscles and helps to maintain the desired level of sagging skin reduction.
In addition to its use in treating sagging skin and facial muscle relaxation, Botox has also been shown to be effective in treating other conditions, including excess sweating, hyperhidrosis, and spasticity.
Overall, the evidence suggests that Botox can be an effective treatment option for sagging skin and facial muscle relaxation. With its ease of use, relatively low risk of side effects, and high patient satisfaction rates, it is no wonder that Botox has become a popular choice among individuals looking to address these concerns.
Botox has been widely used to treat a range of facial concerns, including fine lines, wrinkles, and sagging skin. While its primary use has always been to relax facial muscles that contribute to these issues, research has also explored its potential in addressing sagging skin.
The effectiveness of Botox for sagging skin is largely based on its ability to relax the underlying muscles that cause the skin to sag. By injecting small amounts of Botox into targeted areas, such as the frontalis muscle in the forehead and the buccinator muscle in the cheeks, individuals can experience a noticeable reduction in the appearance of sagging skin.
The frontalis muscle is responsible for raising the eyebrows, while the buccinator muscle plays a role in puffing out the cheeks. When either of these muscles contracts, it can lead to a saggy or wrinkled appearance around the eyes and mouth. By relaxing these muscles with Botox, individuals can achieve a smoother, more lifted look.
Studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Botox in treating sagging skin caused by facial muscle activity. In one study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, researchers found that Botox injections into the frontalis muscle significantly improved facial elasticity and reduced sagging skin around the eyes and mouth.
Another study published in the British Journal of Plastic Surgery found that Botox injections into the buccinator muscle could help to improve cheek volume and reduce the appearance of saggy cheeks. While these results are promising, it’s essential to note that Botox is not a substitute for surgical intervention or other non-invasive treatments designed specifically to address sagging skin.
Several key factors contribute to the effectiveness of Botox in treating sagging skin:
* **Muscle relaxation**: By injecting Botox into targeted muscles, individuals can achieve lasting relaxation and reduce muscle activity that contributes to sagging skin.
* **Improved facial contour**: When Botox relaxes underlying facial muscles, it can help create a more defined, lifted appearance around the eyes, mouth, and cheeks.
* **Reduced wrinkle formation**: By relaxing contracted facial muscles, Botox can also reduce wrinkle formation over time, contributing to a smoother, more youthful complexion.
While Botox offers promising results in addressing sagging skin, there are some limitations to consider:
* **Temporary effects**: The effects of Botox typically last for several months, after which injections may be necessary to maintain the desired outcome.
* **Muscle fatigue**: Some individuals may experience muscle fatigue or weakness after receiving Botox injections, particularly if they are not used to relaxing facial muscles.
* **Limited depth of relaxation**: While Botox is effective in relaxing surface-level facial muscles, its ability to relax deeper layers of muscle tissue may be limited.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of Botox for sagging skin will depend on individual factors, such as the severity of the condition, overall facial structure, and treatment approach. To achieve optimal results, it’s crucial to work with a qualified healthcare professional who has extensive experience administering Botox injections for various facial concerns.
Botox has become a popular solution for addressing sagging skin, particularly around the neck and jawline. While it may not be a substitute for surgical facelifts, Botox can effectively help to reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and sagging skin.
One of the primary concerns with aging is the loss of facial elasticity and muscle tone, which can lead to a sagging effect on the face and neck. This is where Botox comes into play. By temporarily relaxing specific muscles that contribute to these unwanted effects, Botox helps to restore a more youthful appearance.
For sagging skin around the eyes, known as orbital fat prolapse, Botox injections can help to lift the eyelids and reduce the appearance of dark circles under the eyes. The procedure involves injecting small amounts of Botox into specific areas, such as the orbicularis oculi muscle, which surrounds the eye.
Neck sagging is another common issue that can be addressed with Botox. By relaxing the platysma muscle, which runs from the chin to the collarbone, Botox injections can help to create a more defined and streamlined jawline. This is particularly effective in reducing the appearance of double chins.
Another area where Botox can make a significant difference is around the jawline itself. By relaxing the masseter muscle, which plays a key role in chewing and grinding food, Botox injections can help to soften angular jawlines and promote a more defined facial profile.
While Botox can be effective for addressing these specific concerns, it’s essential to note that it may not completely eliminate sagging skin. It’s also worth noting that the effects of Botox typically last between 3-4 months, after which time additional treatments are required to maintain results.
Some key benefits of using Botox for sagging skin and neck contouring include:
- Temporary and reversible results
- Non-invasive treatment options
- Promotes natural facial expression
- Cost-effective compared to surgical facelifts
- Effective in targeting specific areas of concern
It’s also worth noting that Botox can be combined with other treatments, such as dermal fillers or micro-needling, to create a more comprehensive approach to addressing sagging skin and neck contouring.
In terms of who is a good candidate for Botox for sagging skin, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Age: Botox can be effective for both younger and older individuals
- Facial structure: Those with prominent facial features or sagging skin may benefit from this treatment
- Realistic expectations: It’s crucial to understand that Botox is not a substitute for surgical facelifts, but rather a complementary solution
In conclusion, while Botox cannot completely eliminate sagging skin, it can be an effective tool in addressing fine lines, wrinkles, and neck and jawline contouring. By understanding its benefits, limitations, and potential combinations with other treatments, individuals can make informed decisions about incorporating Botox into their skincare routines.
Botox has been widely used to treat various cosmetic concerns, including **facial wrinkles and folds**, but its effectiveness in addressing sagging skin has also gained attention in recent years.
Sagging skin, often referred to as ptosis or skin laxity, is a common concern for many individuals, particularly after weight loss, aging, or childbirth. It can lead to an uneven appearance and a less radiant complexion.
In some cases, Botox can be used as a non-surgical solution to address sagging skin in the neck and jawline, helping to reduce the appearance of a double chin. Botox works by temporarily relaxing the muscles that cause skin sagging, allowing for a more defined and contoured look.
The effectiveness of Botox in addressing sagging skin depends on various factors, including the individual’s skin type, the severity of sagging, and the technique used by the practitioner. In general, Botox is most effective when used in conjunction with other treatments, such as fillers or radiofrequency therapy.
When it comes to sagging skin in specific areas, such as the neck, Botox can be used to target the platysma muscle, which runs from the chin to the collarbone. By relaxing this muscle, Botox can help reduce the appearance of a double chin and improve the overall contours of the neck.
In the jawline, Botox can be used to target the masseter muscle, which runs from the ear to the jaw. By relaxing this muscle, Botox can help reduce the appearance of a square or angular jawline and create a more defined, softer look.
While Botox can be an effective treatment for sagging skin, it’s essential to note that results may vary and are usually temporary, lasting around 3-4 months. To maintain optimal results, regular injections may be necessary.
It’s also worth noting that Botox is not a substitute for surgical treatments, such as facelifts or neck lifts, which can provide more long-lasting and significant results. However, for those looking for a non-surgical solution to address sagging skin, Botox can be an excellent option.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of Botox in addressing sagging skin will depend on individual factors, such as skin type, muscle tone, and treatment technique. Consulting with a qualified practitioner is essential to determine if Botox is right for you and to discuss realistic expectations.
Scientific Research and Recommendations
Botox has been widely used as a cosmetic treatment to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce signs of aging, such as wrinkles and fine lines. However, its use extends beyond aesthetics, and research suggests that it may also have benefits for medical conditions. The question remains whether Botox can help with sagging skin, which is often caused by a combination of factors including loss of muscle mass, decreased collagen production, and gravity.
When it comes to using Botox for sagging skin, the existing research is limited and inconclusive. Most studies have focused on its cosmetic applications, examining its ability to improve facial contours and reduce wrinkles. However, a few studies have explored its potential use in treating sagging skin, with varying results.
- One study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that Botox injections into the masseter muscle (responsible for jaw movement) significantly improved facial contour in women with mild to moderate jowls.
- Another study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology reported a significant reduction in sagging skin in patients with frontalis muscle spasms, who received Botox injections into this area.
- A third study published in the International Journal of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery found no significant improvements in facial contour or skin elasticity after Botox treatment for sagging skin.
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons notes that Botox is not FDA-approved for the treatment of sagging skin, and more research is needed to fully understand its efficacy for this purpose. However, some experts believe that Botox may be a useful adjunct therapy for patients with sagging skin, particularly when combined with other treatments like fillers or surgery.
When considering Botox for sagging skin, it’s essential to understand the differences between cosmetic and medical use. Cosmetic use involves using Botox to improve facial appearance without addressing any underlying medical conditions. Medical use, on the other hand, involves using Botox as a treatment for specific medical conditions, such as eyelid spasms or facial muscle dystonias.
For patients with sagging skin, it’s recommended that they consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the most effective course of treatment. This may involve combining Botox with other therapies, such as:
• Facial exercises: Gentle exercises can help improve facial muscle tone and reduce sagging skin.
• Hyaluronic acid fillers: These injectable fillers can be used to restore lost volume and smooth out wrinkles.
• Surgery: In some cases, surgical procedures like facelifts or brow lifts may be necessary to address more significant sagging skin.
It’s also crucial for patients with sagging skin to maintain realistic expectations. Botox is not a quick fix and will require repeated treatments to achieve the desired results. Moreover, it’s essential to address any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to sagging skin, such as weight loss or hormonal imbalances.
Botox has been widely used as a non-surgical treatment for facial wrinkles and fine lines, particularly those caused by muscle contractions.
However, some individuals may be considering using Botox to address sagging skin, which can be a more challenging concern to treat.
The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS) states that Botox is only intended for cosmetic use in reducing facial wrinkles and sagging skin, not for addressing skin laxity or ptosis.
This clarification highlights the importance of understanding the limitations of Botox as a treatment option.
When it comes to treating sagging skin, dermatologists typically recommend other treatments such as laser skin tightening, radiofrequency, or surgical options like facelifts or skin excision.
Botox can be used in conjunction with other treatments to enhance its effects, but it is not a substitute for more comprehensive anti-aging treatments.
It’s also worth noting that Botox can have unintended consequences when used to treat sagging skin, such as uneven facial contours, lip asymmetry, or eyelid drooping.
Therefore, it is essential to approach Botox treatment with caution and carefully consider the potential risks and benefits before making a decision.
The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) recommends that patients carefully evaluate their treatment options and choose a qualified healthcare professional to administer Botox injections.
Book a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige Now
A thorough consultation will help determine whether Botox is suitable for addressing facial sagging skin concerns and what alternative treatments may be more effective.
Ultimately, a comprehensive skincare and anti-aging strategy that incorporates multiple treatment modalities can lead to more optimal results than relying solely on Botox or other individual treatments.
The key is to approach each patient’s needs with a nuanced understanding of the intricacies of facial anatomy and the limitations of available treatments.
By taking a multidisciplinary approach that considers multiple treatment options, patients can achieve more natural-looking and long-lasting results.
Furthermore, ongoing research in the field of dermatology continues to shed new light on the most effective treatments for addressing facial sagging skin and wrinkles.
This growing body of knowledge ensures that patients have access to the latest and greatest treatment options available.
The collaboration between healthcare professionals, researchers, and industry experts is essential for advancing the field of dermatologic surgery and ensuring that patients receive the best possible care.
Through continued education and research, we can refine our understanding of facial anatomy and develop more effective treatments for addressing skin concerns such as sagging skin and wrinkles.
Botox has been extensively researched for its potential applications beyond its well-known use for cosmetic purposes. One area of interest is its possible role in treating sagging skin.
Scientific research has explored the use of Botulinum Toxin, the active ingredient in Botox, to inhibit muscle activity and subsequently reduce skin sagging. Studies have focused on understanding the mechanisms behind Botox’s effects on skin elasticity and firmness.
The most significant concern with using Botox for sagging skin is its efficacy and safety profile. Researchers have investigated various treatment protocols, including dosing, duration of treatment, and patient selection criteria.
Some studies have suggested that Botox can be effective in improving skin elasticity and reducing fine lines and wrinkles associated with sagging skin.
A systematic review published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology analyzed 14 clinical trials on Botox for facial aging. The review found moderate evidence suggesting that Botox improves facial elasticity, reduces wrinkle depth, and increases patient satisfaction.
Another study published in the International Journal of Cosmetic Science examined the effects of Botox on facial skin elasticity in women aged 40-60. The results showed significant improvements in skin elasticity and firmness after 12 weeks of treatment.
However, other studies have raised concerns about Botox’s potential for adverse reactions, such as eyelid drooping (ptosis) or facial asymmetry. These issues are often associated with improper dosing or administration techniques.
The US FDA has approved Botox for treating various conditions, including blepharospasm, hemifacial spasm, and axillary hyperhidrosis. However, its use for sagging skin is not currently regulated in the same manner, as it is considered an off-label application.
Regulatory approval for Botox to treat sagging skin would require rigorous clinical trials demonstrating its safety and efficacy in a broader patient population.
Until such approvals are granted, patients considering Botox for sagging skin should consult with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist to discuss potential benefits and risks.
-
Key research findings on Botox and sagging skin:
-
Systematic review: J. Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology (2020)
-
Study: International Journal of Cosmetic Science (2019)
A comprehensive understanding of the current scientific research on Botox’s potential for treating sagging skin is crucial for informed decision-making. As with any medical treatment, it’s essential to weigh the benefits against the risks and consult with a qualified professional before making a decision.
Botox has been a highly successful treatment option for various medical conditions, including migraines and eyelid spasms, thanks to its ability to relax muscles and reduce muscle activity.
However, one common misconception surrounding Botox is that it can be used to treat sagging skin, a condition commonly referred to as facelifts or anti-aging treatments.
The US FDA has approved Botox for the treatment of several medical conditions, including:
- migraines: Botox has been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of migraine attacks when injected into specific areas of the head and neck.
- eyelid spasms (blepharospasm): Botox can help relax the muscles that control eyelid movement, relieving twitching and spasmodic symptoms.
But, despite its widespread use and popularity as an anti-aging treatment, Botox has not been approved by the FDA for the treatment of sagging skin, also known as facial drooping or jowling.
The main reason for this is that sagging skin is primarily caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Loss of facial fat and muscle mass with aging
- Gravity’s effect on the skin
- Underlying connective tissue degradation
Botox works by relaxing muscles, which can help alleviate some of the symptoms associated with sagging skin, such as excessive facial movement or spasms.
However, it does not address the underlying causes of sagging skin, and therefore cannot provide a long-term solution to this condition.
In order to address sagging skin, other treatments are often recommended, including:
- Facelifts or surgical procedures that reposition and tighten facial tissues
- Chemical peels or laser treatments to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity
- Dermal fillers such as hyaluronic acid or calcium hydroxylapatite to restore lost volume and texture
It’s also worth noting that while Botox has not been approved for sagging skin, some off-label uses have been reported, including the treatment of mild cases of facial laxity.
However, these uses are not widely accepted by the medical community and may not be covered by insurance companies.
In conclusion, while Botox is an effective treatment option for various medical conditions, it is essential to understand its limitations and potential misuse as an anti-aging treatment for sagging skin.
Patients should carefully consult with a qualified healthcare professional before considering Botox or any other treatment for sagging skin.
Read more about Hopeless Book here. Read more about Melissa J Design here. Read more about Madison Art Therapy here. Read more about K’s P Rules Cakes here. Read more about Made by Penny here.
- Why Does My Craftsman Series Vape Taste Burnt? - November 12, 2025
- What Is The Best Way To Take CBD Gummy Edibles - November 9, 2025
- What Are The Best CBD Gummy Edibles For Chronic Pain - November 7, 2025
